Uniform motion & Non-Uniform motion
Uniform motion & Non-Uniform motion
Uniform motion : An object is said to be moving with uniform velocity if it covers equal displacements in equal intervals of time, however small these intervals may be.
Or,
Another word we can say that, A body is said to have uniform motion when it travels equal distances in equal intervals of time.
Uniform motion of a body is illustrated.
Time
Example: A body moving with a constant speed is said to be in uniform motion.
The study of the uniform motion is the simplest one. An accelerated motion requires a cause or an effort. Uniform motion in a straight line is physically important from the point of view that it does not require any such cause of effort.
Now,
velocity of the uniform motion = displacement / time interval
V = x’- x / t’-t
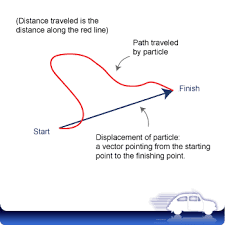
Non-Uniform motion: A body is said to have non-uniform motion when it travels unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
The non-uniform motion of a body is illustrated.
Key point
1. No force is required to keep an object in uniform motion .
2. When an object has uniform motion along a straight line in a given direction, the magnitude of displacement is equal to actual distance covered.
3.The velocity of uniform motion is same for different choices of t and t’.
4.The position value of velocity means that the motion is towards right of the origin, while the negative velocity means that the motion is towards the left of the origin.
5.For an object to be in uniform motion, no cause or effort i.e. no force is required.
6. Since the velocity during uniform motion is same at each point of the path or at each instant, average and instantaneous velocities in a uniform motion are always equal.
7.The velocity-time graph for an object having uniform velocity is a straight line parallel to time-axis.



Comments
Post a Comment