Motion in Physics Velocity part2
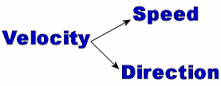
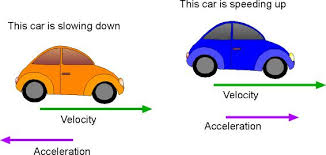
Motion in Physics Velocity part2 continues.. When is velocity said to have change Velocity is a vector quantity. So, velocity has a magnitude as well as a direction. The magnitude of velocity is equal to the speed of the body. If either of the two, i.e., either speed or direction changes, velocity is said to have changed. Thus, the velocity of a body change due to a change in its speed, its direction, or both . Let us consider a car travelling (towards east) at a constant speed of 10 m/s. Then, it has a constant velocity in that direction. When the takes a turn, its velocity changes although its speed remains constant. When the car is at right angles to its original direction, the its velocity (towards east) becomes zero, the speed remaining constant. When the car is travelling in the direction just opposite to the original direction, it has a negative velocity. So, the velocity of a moving object changes due to a change in its direction. What is meant by...